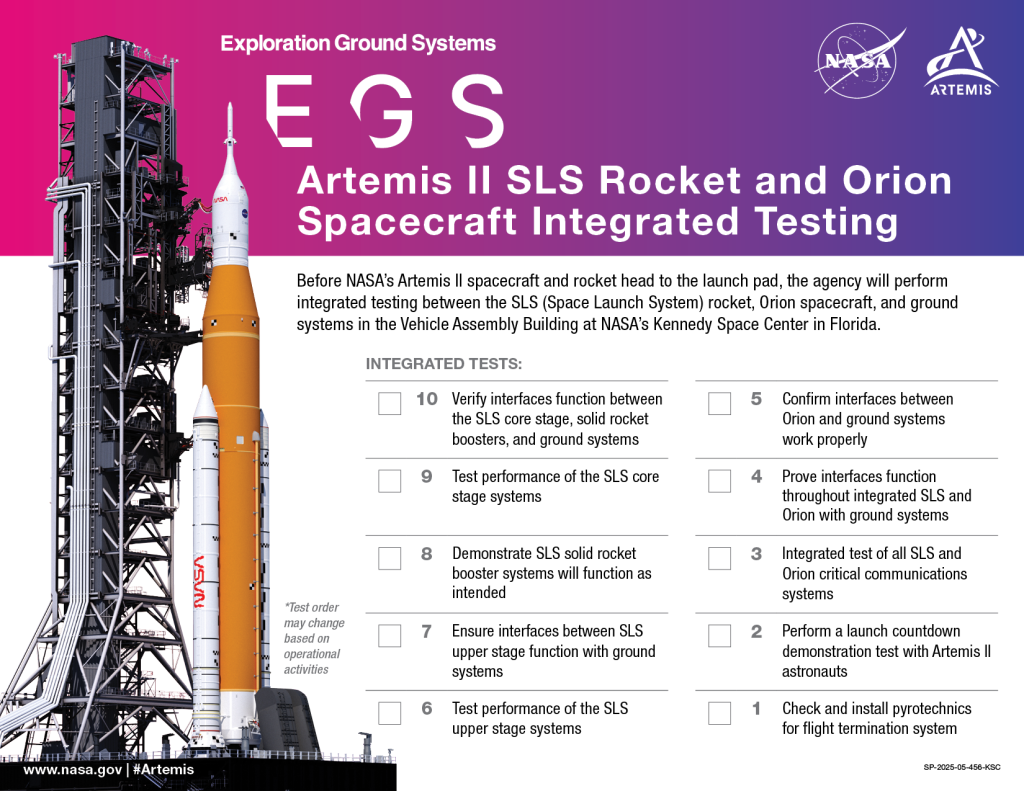
1 min read
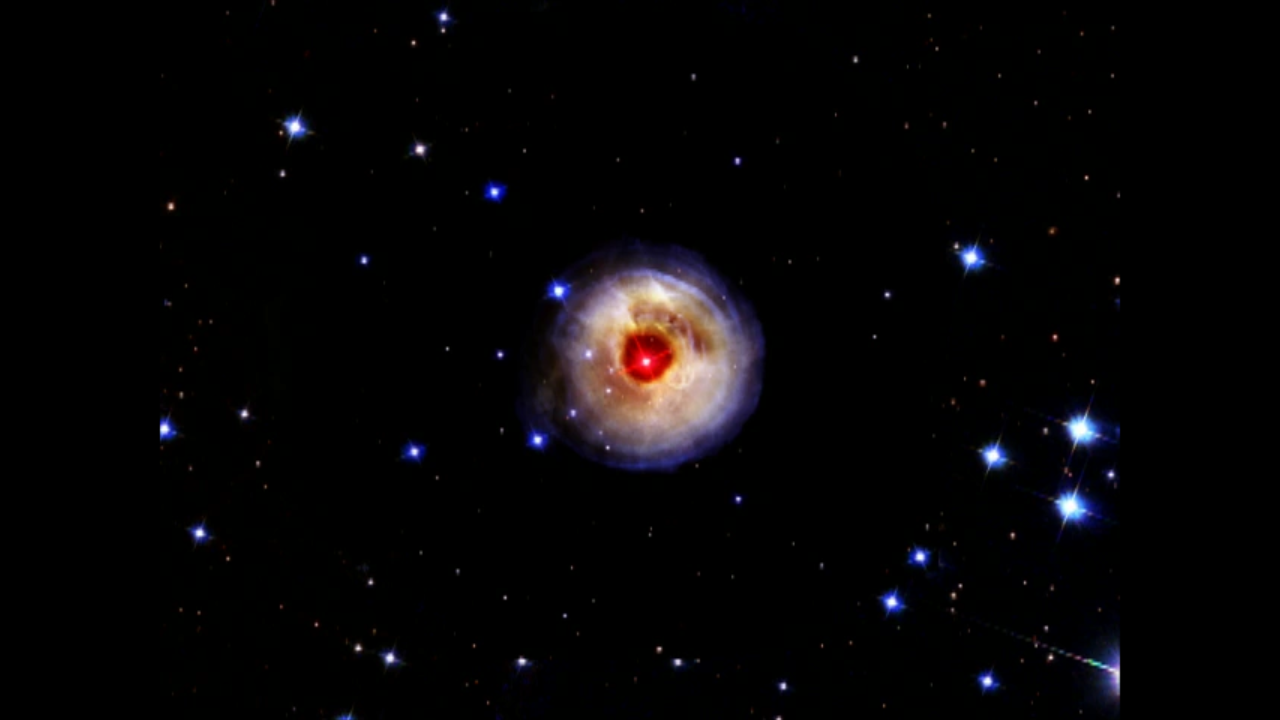
V838 Monocerotis – September 2006

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.07h 4m 4.99s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-3° 50' 50.0"
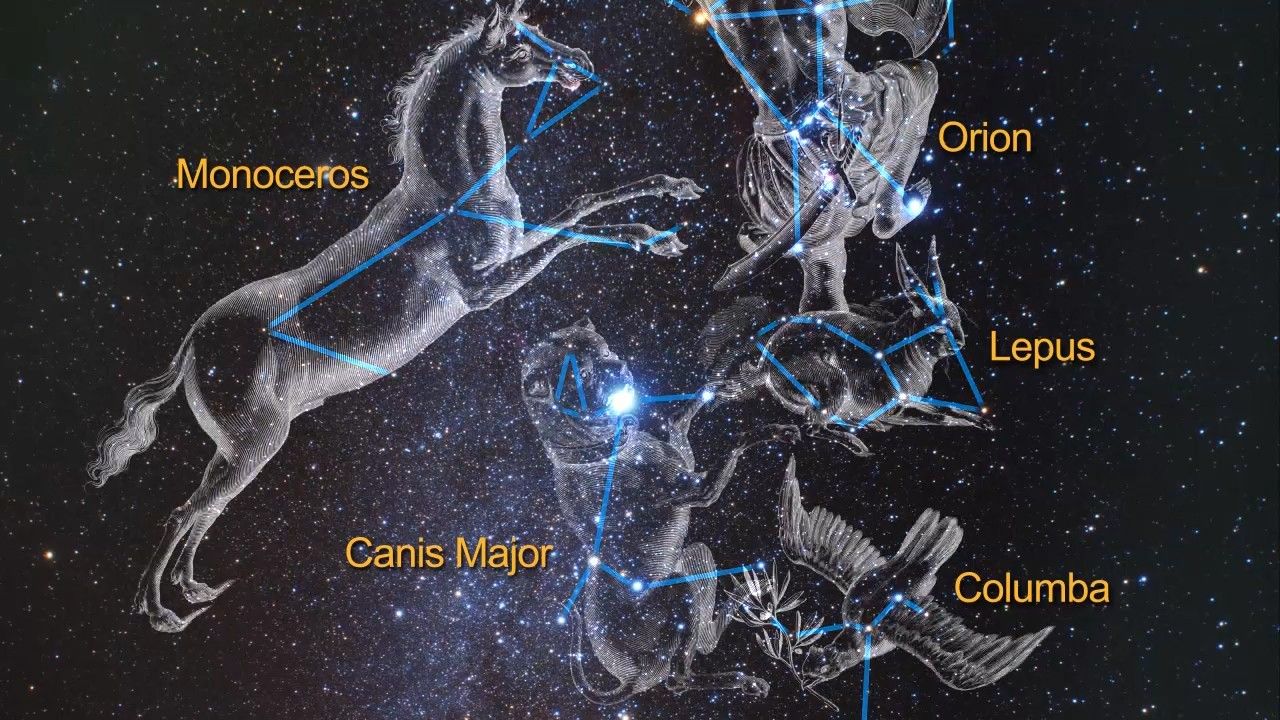
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Monoceros
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.The star is ~20,000 light-years (~6 kiloparsecs) away.
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.2.5 arcminutes (14 light-years or 4.5 parsecs) wide
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from the following proposals: 10618 and 10913: H. Bond (STScI), R. Wagner (University of Arizona), R. White (STScI), R. Corradi (Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos), L. Crause (University of Cape Town), M. Dopita (Australian National University), A. Henden (United States Naval Observatory), Z. Levay (STScI), U. Munari (Universita di Padova), N. Panagia (STScI/ESA), W. Sparks (STScI), S. Starrfield (Arizona State University), and B. Sugerman (STScI). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.September 9, 2006
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F606W (V) and F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.V838 Monocerotis, V838 Mon
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Nova-like variable star and surrounding light echo
- Release DateOctober 26, 2006
- Science ReleaseHubble’s Latest Views of Light Echo from Star V838 Monocerotis
- Credit

This image is a composite of many separate exposures made by the ACS instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope. Two filters were used to sample broad wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic image. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F606W (V) Greed: F606W (V) + F814W (I) Red: F814W (I)

Related Images & Videos

Hubble's Latest Views of Light Echo from Star V838 Monocerotis
These are the most recent NASA Hubble Space Telescope views of an unusual phenomenon in space called a light echo. Light from a star that erupted nearly five years ago continues propagating outward through a cloud of dust surrounding the star. The light reflects or "echoes" off...

V838 Monocerotis Dissolve Sequence of Epochs
A dissolve sequence of eight images taken by Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys shows a CAT-scan-like probe of the three-dimensional structure of the shells of dust surrounding the aging star V838 Monocerotis. The sequence reveals dramatic changes in the way a brilliant flash...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov